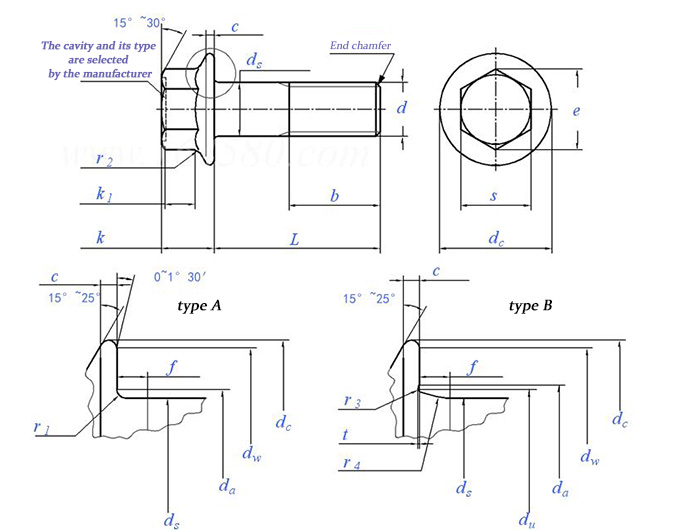
Flange bolts and flange nuts are key components in the connection of pipeline systems and pressure vessels. Their structural features are reflected in the integrated flange surface at the bolt head or the bottom of the nut. This integrated design combines the functions of traditional bolts and flat washers. The diameter of the flange surface is usually 2.5-3 times the diameter of the bolt. For example, the diameter of the flange surface of the M20 bolt is mostly in the range of 50-60mm, which effectively reduces the compressive stress of the connection surface by increasing the contact area. According to the ASME B18.2.6 standard, the hexagonal opposite side size of the flange bolt is increased by about 15% compared with ordinary bolts to match the structural strength of the flange surface.
In terms of technical parameter selection, the strength grade of flange bolts is generally required to reach 8.8 or 10.9, and the tensile strength is not less than 800MPa and 1040MPa respectively. For high temperature and high pressure conditions, alloy steel bolts made of ASTM A193 Gr.B7 are often used, which can maintain stable performance under 450℃ environment. The matching flange nuts must meet the principle of equal strength matching. Typical specifications include ASTM A194 Gr.2H, and the hardness is controlled between HRC22-32. In terms of surface treatment technology, Dacromet coating can provide more than 1000 hours of salt spray protection, while the thickness of the hot-dip galvanized layer is usually controlled at 50-80μm, ensuring more than 10 years of corrosion resistance in outdoor environments.
The typical application scenarios of this type of fasteners are concentrated in connection parts that require high sealing and vibration resistance. Flange bolt sets are commonly used in pipeline flange connections in the petrochemical industry. In pipelines above DN300, each flange plate needs to be equipped with 16-24 sets of bolts, and the preload force needs to be controlled within 30%-70% of the yield strength of the bolt material. The flange connection of rotating equipment such as turbines and compressors emphasizes anti-loosening performance. At this time, when used with Spirax anti-loosening nuts, the preload force loss under vibration conditions can be controlled within 5%. For heat exchanger flanges with thermal expansion, it is necessary to calculate the thermal stress at the working temperature and select bolt materials with matching thermal expansion coefficients. For example, the thermal expansion coefficient of 304 stainless steel bolts is 17.3×10^-6/℃. When there is a difference with carbon steel flanges, compensation calculations need to be performed.
From the perspective of use benefit analysis, the main advantage of flange bolts is the uniformity of contact pressure distribution. The flange surface reduces the stress concentration factor by about 40%, which is particularly suitable for the connection of low-strength materials such as cast iron and plastic. At the same time, the integrated design reduces the number of parts and can reduce the installation time by 30% compared with the traditional bolt gasket combination in the DN500 flange connection. However, the limitations are also obvious. The flange surface structure increases the weight of a single piece by 20%-25%, which may affect the installation in compact equipment with limited space. In terms of cost, the price of flange bolts of the same specification is 15%-30% higher than that of ordinary bolts, but in the inspection port position where frequent disassembly is required, its anti-seizure performance can reduce maintenance costs. In practical applications, it should be noted that the parallelism error between the flange surface and the connection surface should be less than 0.05mm, otherwise it may cause unilateral overload and cause early failure.
Post time: Mar-25-2025